Germ Cell Tumor
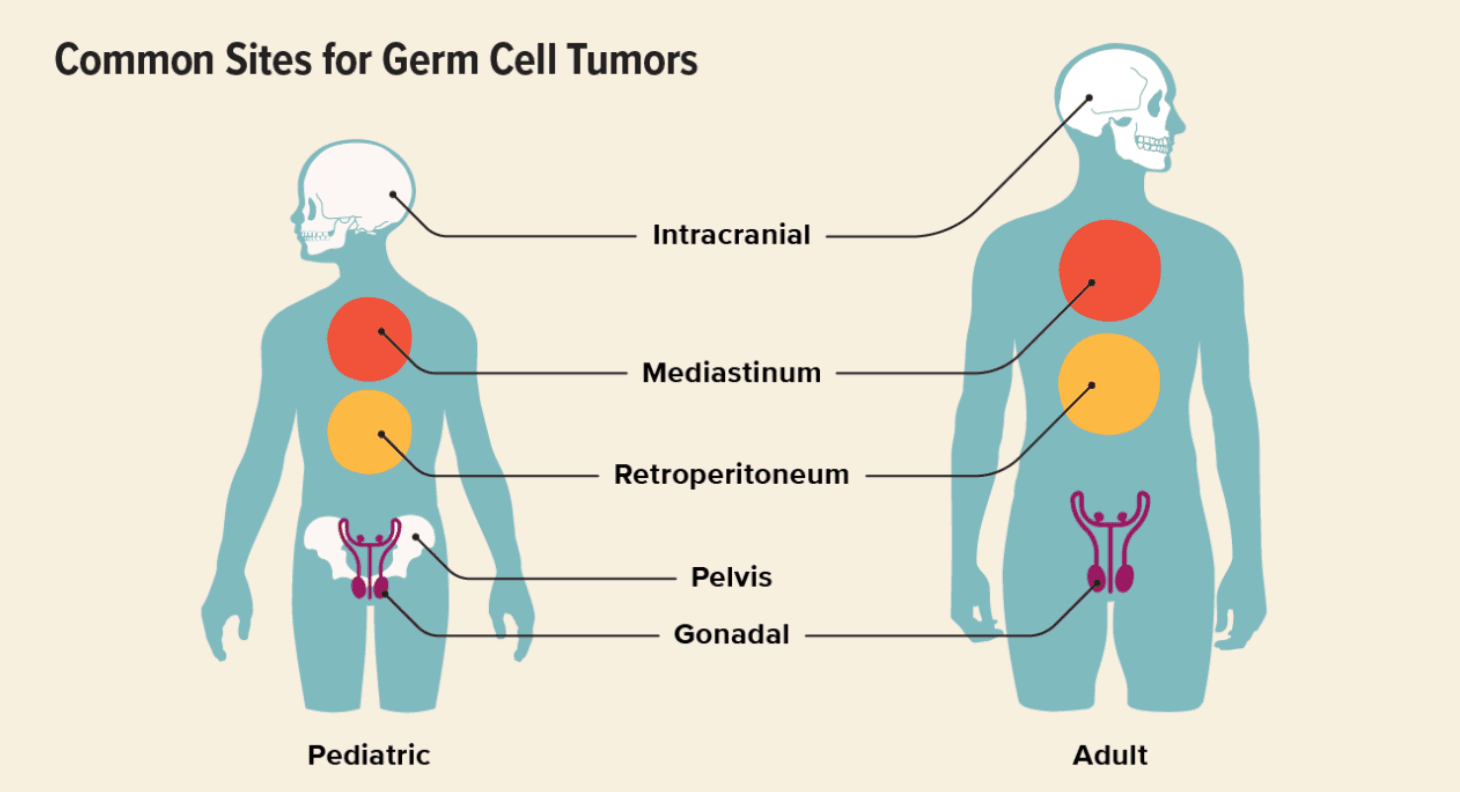
Germ cells, also called gametes, are specialized cells responsible for sexual reproduction. Their name comes from the word germinate, meaning “to begin to grow.” During fetal development, germ cells migrate to specific locations and later develop into sperm in males or egg cells (ova) in females. In some cases, germ cells undergo abnormal growth and form a germ cell tumor (GCT). These tumors most commonly develop in the testicles or ovaries, but in rare cases, they can appear in other parts of the body. Germ cell tumors are rare and most often occur in adolescents and young adults between ages 15 and 30, though they can affect children and older adults as well. Types of Germ Cell Tumors Germ cell tumors can be classified by behavior, sex, and location. By Behavior Benign (non-cancerous) Malignant (cancerous) By Sex In males (testicular germ cell tumors): Seminoma Non-seminoma In females (ovarian germ cell tumors): Dysgerminoma Non-dysgerminoma Other Germ Cell Tumor Types Teratoma (benign or malignant) Choriocarcinoma Germinoma Embryonal carcinoma Endodermal sinus tumor (yolk sac tumor) Polyembryoma Mixed germ cell tumors Extragonadal Germ Cell Tumors In rare cases, germ cell tumors develop outside the ovaries or testicles. These are called extragonadal germ cell tumors and may appear in: Mediastinum (chest) Pineal region of the brain Retroperitoneum (back of the abdomen) Sacrococcygeal area (base of the spine) Causes and Risk Factors The exact cause of germ cell tumors is not fully understood, but several factors increase risk: Genetic syndromes (e.g., Turner syndrome, Klinefelter syndrome) Birth defects involving the genitals, spine, or urinary tract Cryptorchidism (undescended testicle) Age, especially males aged 15–35 and adolescent girls or young women Germ Cell Tumor Symptoms Symptoms depend on the tumor’s type and location. Ovarian Germ Cell Tumors Abdominal swelling Pelvic pain Constipation Irregular vaginal bleeding Testicular Germ Cell Tumors Testicular lump or swelling Groin pain Heaviness in the scrotum Extragonadal Germ Cell Tumors Breathing difficulty (mediastinal tumors) Urinary problems Leg weakness or neurological symptoms (spinal involvement) Diagnosis Early detection is critical. Diagnostic tests may include: Physical examination Imaging tests (ultrasound, CT scan, MRI) Blood tests (tumor markers such as AFP, β-hCG, LDH) Biopsy or surgical removal for definitive diagnosis Germ Cell Tumor Staging Staging determines how far the tumor has spread and guides treatment. Stage 1 Tumor confined to the original site Often treated with surgery alone Stage 2 Spread to nearby tissues or structures Still localized to the pelvic or regional area Stage 3 Spread to distant areas or regional lymph nodes Stage 4 Metastasis to distant organs Common sites: lungs, liver, distant lymph nodes Germ Cell Tumor Treatment Treatment is individualized based on tumor type, stage, and patient factors. Surgery First-line treatment for localized tumors May involve removal of the tumor and, if necessary, the affected ovary or testicle Fertility-sparing surgery is often possible Chemotherapy Highly effective because germ cell tumors are very chemo-sensitive Used for advanced, aggressive, or metastatic disease Radiotherapy may be added in select cases Immunotherapy Used in relapsed or chemotherapy-resistant tumors Helps the immune system target cancer cells Prognosis Germ cell tumors generally have an excellent prognosis, especially when diagnosed early. Testicular germ cell tumors: ~95% survival rate Ovarian germ cell tumors: ~93% survival rate Outcomes depend on tumor location, stage at diagnosis, response to treatment, and overall patient health.
Patients served
Countries
Clinics
Experienced doctors
Your Benefits and Guarantees with Amedical
Experience a seamless and secure breast lift journey with Amedical.Transparent Prices and Flexible Installment Plans
No hidden fees — only official clinic prices. You can pay for your breast lift directly at the clinic upon arrival and use a flexible installment plan if needed.
Verified Clinics and Doctors Only
Amedical is fully committed to your safety. We cooperate exclusively with medical institutions that meet high international standards in breast lift procedures and are licensed to serve international patients.
Free 24/7 Support Service
Amedical provides free expert assistance. Your personal medical coordinator supports you before, during, and after your treatment, helping to resolve any issues. You are never alone on your breast lift journey.

Your personal AMedical medical coordinator
Supports you at every stage
Helps choose the right clinic and doctor
Ensures quick and convenient access to information
Loading clinics...
Our Trusted Doctors
Our doctors are highly skilled and experts in their fields.

Orthopaedic surgeon and pediatric traumatologist Languages: English, Spanish, Catalan, Portuguese

Orthopaedic surgeon and pediatric traumatologist Languages: English, Spanish and Catalan

Paediatric surgeon Languages: Spanish, Catalan, English and French
Related Articles
Stay informed with our latest medical insights and health tips

How Pick the Best Clinics for Gastric Sleeve Surgery in Turkey
Gastric sleeve surgery in Turkey is a popular weight loss procedure that involves removing a portion of the stomach to reduce its capacity.
8 Best and Cheapest Countries for Dentures 2025
The best and cheapest countries for veneers or best and cheapest countries for dental prostheses include Turkey, Thailand, and Mexico, where clinics offer modern technology, experienced specialists, a...

Rehabilitation After Stroke in Switzerland
Rehabilitation after stroke in Switzerland provides a structured, patient-centered recovery pathway that combines advanced neurorehabilitation, personalized therapy plans, and a supportive healing env...
Country Treatment
Find the best treatment options available in your country.
Get a free consultation
Talk to our experts and discover the best solution for your needs completely free of charge.
