Contents
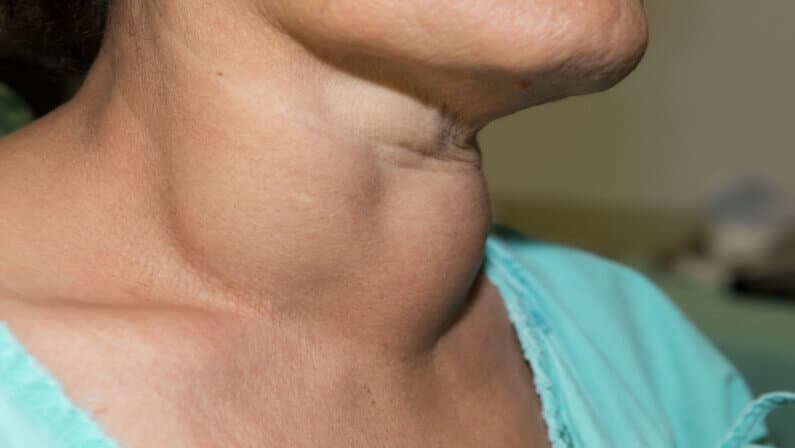
Thyroid disease is a condition that occurs when the thyroid gland produces too much or too little hormone. The thyroid gland is a small, butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck that produces hormones that regulate metabolism. When the thyroid gland produces too much hormone, it causes hyperthyroidism, and when it produces too little hormone, it causes hypothyroidism.
Turkey is a popular destination for medical tourism and is no exception when it comes to treating thyroid disease. Turkey has a reputation for providing high-quality medical care at a fraction of the cost compared to other countries. The country has modern facilities and highly trained doctors who use the latest technology to diagnose and treat thyroid disease.
What is thyroid disease?
Thyroid diseases are conditions that affect the thyroid gland, which is a butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck. The thyroid gland produces hormones that regulate the body's metabolism, growth, and development. When the thyroid gland produces too much or too little of these hormones, it can lead to a variety of health problems.
Types of thyroid disorders
There are several types of thyroid disorders, including:
- Hypothyroidism: This is a condition in which the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormone. Symptoms of hypothyroidism can include fatigue, weight gain, constipation, dry skin, and depression.
- Hyperthyroidism: This is a condition in which the thyroid gland produces too much thyroid hormone. Symptoms of hyperthyroidism can include weight loss, rapid heartbeat, anxiety, irritability, and sweating.
- Thyroid nodules: These are lumps that form in the thyroid gland. Most thyroid nodules are benign, but some can be cancerous.
- Thyroid cancer: This is a rare type of cancer that develops in the thyroid gland.
Symptoms and diagnosis of thyroid disease
The symptoms of thyroid disorders can vary depending on the type of disorder. Some common symptoms include:
- Fatigue
- Weight changes
- Hair loss
- Muscle weakness
- Irregular menstrual periods
- Difficulty sleeping
- Anxiety or depression
Diagnosis of thyroid disorders typically involves a physical exam, blood tests to measure thyroid hormone levels, and imaging tests such as ultrasound or a thyroid scan. In some cases, a biopsy may be needed to determine if a thyroid nodule is cancerous. Treatment for thyroid disorders include medication, surgery, or radioactive iodine therapy.
Treatment methods of thyroid Disease in Turkey
When it comes to treating thyroid disease, Turkey offers a variety of treatment modalities. These include medication and hormone therapy, radioactive iodine treatment, and surgery options.
Medication and hormone therapy
Medication and hormone therapy are often the first line of treatment for thyroid disease. In Turkey, doctors prescribe medications such as levothyroxine, liothyronine, and antithyroid drugs to help regulate thyroid hormone levels. These medications can help manage symptoms such as fatigue, weight gain, and sensitivity to cold.
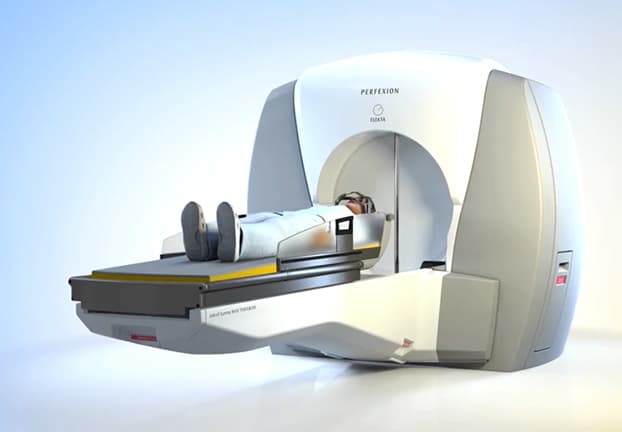
Radioactive iodine treatment
Radioactive iodine treatment is a common treatment option for hyperthyroidism in Turkey. This treatment involves taking a radioactive iodine pill, which is absorbed by the thyroid gland and destroys thyroid cells. The treatment is often used for patients with Graves' disease or toxic multinodular goiter. Patients may need to take thyroid hormone replacement medication after the treatment.
Surgery options
Surgery is another treatment option for thyroid disease in Turkey. The most common surgery is a thyroidectomy, which involves removing all or part of the thyroid gland. This surgery is often recommended for patients with thyroid cancer, large goiters, or hyperthyroidism that cannot be managed with medication or radioactive iodine treatment.
Thyroid cancer treatment in Turkey
Thyroid cancer occurs when cells in the thyroid gland become cancerous, forming abnormal growths in the neck or nodules within the gland.
In Turkey, the primary treatment for thyroid cancer is surgery, which involves removing all or part of the thyroid gland. Following surgery, radioactive iodine therapy is administered to prevent the cancer from recurring.
After thyroid surgery, lifelong oral thyroid hormone therapy is provided to fulfill the body's hormone requirements and prevent the cancer from returning.
In extremely rare instances, treatments like radiotherapy and chemotherapy may be necessary for thyroid cancer.
Why is Turkey the best country for thyroid treatment?
Turkey excels in medical tourism due to its affordable prices and top-notch medical services. Patients opt for Turkey for thyroid treatment because it offers:
- Affordable treatment
- Availability of effective treatment methods found in many countries
- Access to renowned doctors and surgeons
- Minimal waiting times for treatment
- Treatment in JCI accredited clinics
Choosing Turkey over countries like the UK, Germany, and the United States for thyroid treatment ensures greater advantages. Turkey stands out for providing excellent medical services at reasonable prices.
Turkish clinics employ diverse treatment methods for thyroid conditions, including iodine therapy and surgery, ensuring comprehensive care.
One compelling reason to select Turkey for thyroid treatment is its impressive success rates. Turkish clinics boast a 99% success rate, offering permanent cures for thyroid conditions.
Is Turkey successful in thyroid treatment?
In Turkey, thyroid issues are effectively treated with permanent solutions. Clinics offer a 99% success rate in curing thyroid problems permanently through surgical and iodine therapies.
Best clinics for thyroid treatment in Turkey
Thinking about getting thyroid treatment in Turkey? Start by choosing a clinic and a skilled surgeon for the best results. A-Medical recommends top-notch clinics and doctors to ensure high-quality standards.
Top options for thyroid treatment in Turkey:
- Anadolu Johns Hopkins Medical Center
- Florence Nightingale
- Koç University Hospital
Cost of thyroid treatment in Turkey
Thyroid treatment in Turkey costs between $4,000 to $15,000, varying based on treatment, clinic, and disease severity.