Treatment Abroad – Find Verified Clinics, Reviews & Prices
Treatment Abroad made simple by A-Medical. Explore top clinics worldwide and start your journey toward better health today
We make healthcare abroad
simple, transparent, and fully guided from start to finish
Submit Your Request
Tell us about your treatment needs. We carefully review your case and match you with the most suitable hospitals and doctors.
Get Official Price Quotes
We provide verified treatment offers and proformas directly from hospitals — no middlemen, full transparency.
Connect with Doctors
We arrange direct calls or video consultations with hospitals and doctors so you can discuss your treatment plan confidently.
Confirm & Start Treatment
Once you accept the treatment plan, we schedule your hospital appointment and support you throughout your medical journey.
Clinics
Discover our network of world-class medical facilities offering comprehensive healthcare services
Why Choose Us
With us, you are in safe hands. We focus on quality, transparency, and patient-first care. Here’s what sets us apart
Only Accredited Hospitals
We partner exclusively with internationally accredited and top-ranked hospitals.
Direct & Transparent Payments
You pay directly at the hospital, with no hidden fees.
Free Direct Call & Video Consultation
Speak with our experts and doctors before making any decisions.
Best Doctor & Hospital Match
We carefully select the most suitable specialist and clinic for your treatment needs.
Worldwide Hospital Network
Access to a vast global network across 90+ countries.
More Affordable Pricing
We negotiate better prices from hospitals than you would get by contacting them directly.
Medical Conditions
Explore our comprehensive coverage of medical conditions and find the right treatment options

Ecstasy (MDMA) Addiction
Ecstasy, a synthetic drug, has the properties of both hallucinogenic drugs such as LSD and stimulant substances like amphetamines.
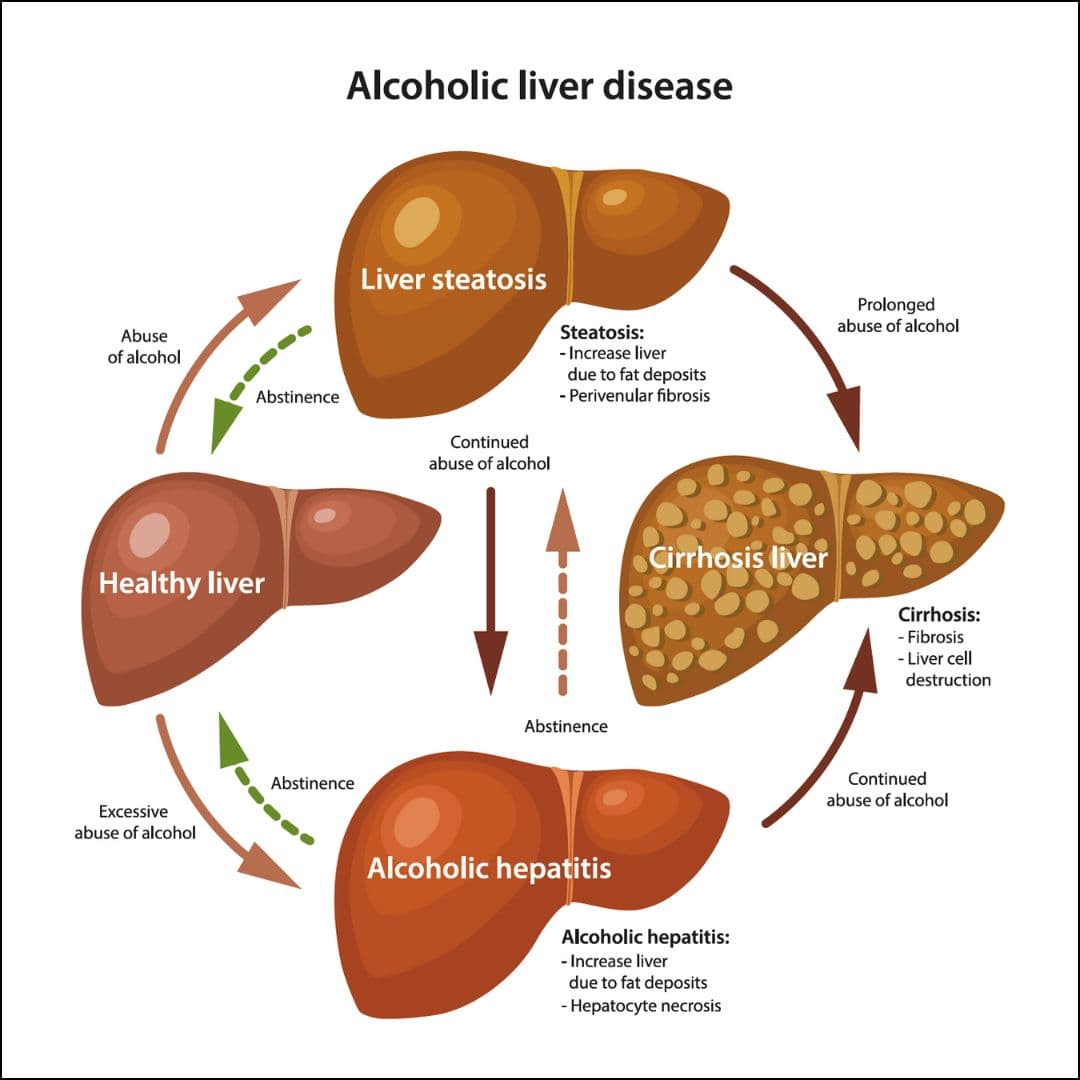
Alcoholic Liver Disease
Alcoholic Liver Disease, also called Alcohol-Related Liver Disease (ARLD), is caused by long-term heavy alcohol use. It develops in stages that range from mild damage to life-threatening complications. Stages Fatty Liver: Early buildup of fat in the liver, often without symptoms. Alcoholic Hepatitis: Inflammation of the liver that can cause nausea, pain, or jaundice. Fibrosis and Cirrhosis: Scarring of the liver, which can progress to permanent and severe damage. Symptoms Early stages may not cause symptoms. As the disease advances, signs can include: Nausea and weight loss Jaundice (yellowing of skin and eyes) Confusion or difficulty thinking Abdominal swelling from fluid buildup
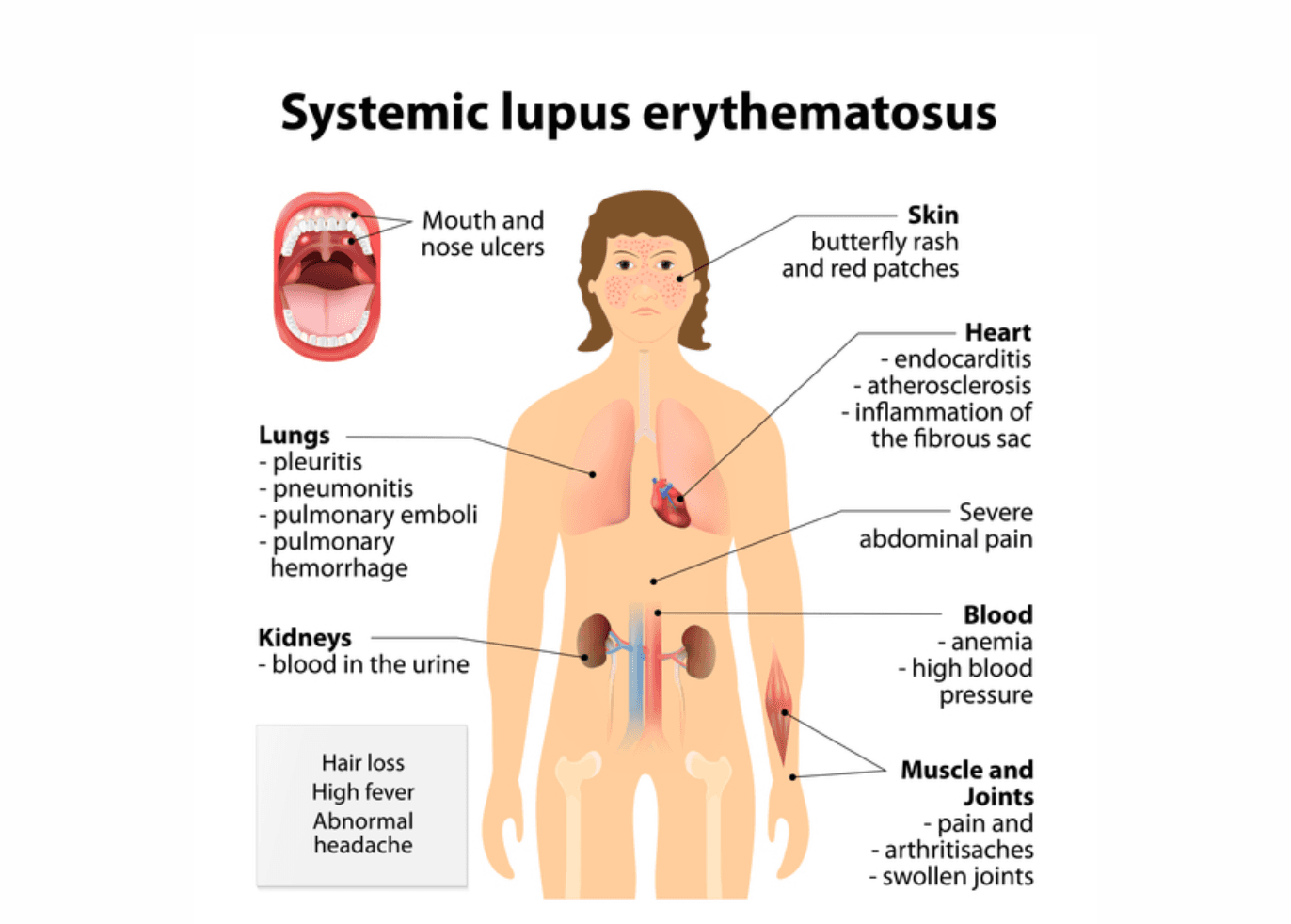
Systemic lupus erythematosus
Systemic lupus erythematosus
Get a free consultation
Talk to our experts and discover the best solution for your needs completely free of charge.

Related Articles
Stay informed with our latest medical insights and health tips
IVF in Turkey: High Success, Low Cost, No Waiting
It’s no coincidence that IVF in Turkey has become a central topic among those researching international fertility options—especially couples looking for effective, transparent, and affordable treatmen...

Best Clinics for Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy for Parkinson’s
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for Parkinson’s disease is a medical treatment where patients breathe pure oxygen in a pressurized chamber to improve oxygen flow to the brain and body.

ALS Treatment in Turkey: Best Clinics and Costs
This article discusses ALS treatment with stem cells in Turkey. For information on costs, top clinics, and procedures, read on.
Our doctor is highly skilled and an expert in their field.









