Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)
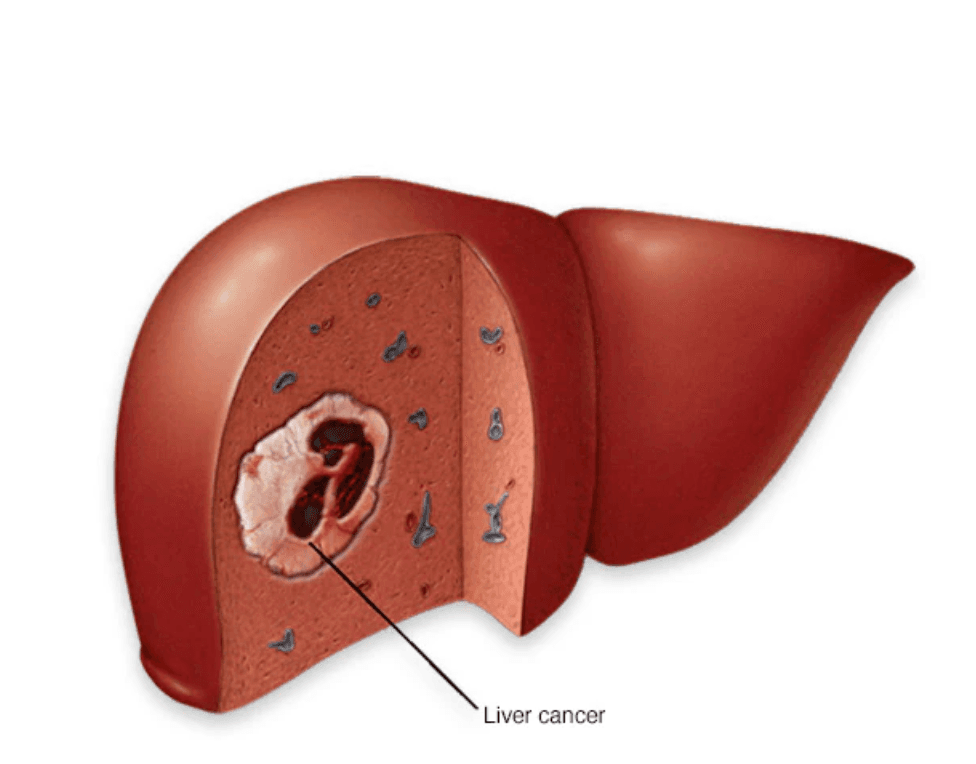
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common type of primary liver cancer. It begins in liver cells called hepatocytes and most often develops in people with chronic liver disease, especially cirrhosis caused by hepatitis B or hepatitis C infection. The liver sits under the right rib cage and plays a vital role in digestion, detoxification and metabolism. In HCC, genetic changes cause liver cells to grow uncontrollably, forming a tumor that can damage healthy liver tissue, invade blood vessels and spread (metastasize) to other organs. Why HCC is dangerous Often causes no symptoms in early stages Commonly occurs in people whose liver function is already poor Frequently diagnosed at an advanced stage Treatment options depend on tumor stage and liver reserve Causes HCC develops when DNA changes occur in hepatocytes, leading to uncontrolled growth. The most common underlying causes include: Cirrhosis Chronic hepatitis B or C Long-standing liver inflammation or injury In some cases, HCC develops without known liver disease, though this is less common. Risk factors Chronic hepatitis B or C Cirrhosis (any cause) Metabolic dysfunction–associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD/MASH) Diabetes and obesity Heavy alcohol use Smoking Inherited liver diseases (hemochromatosis, Wilson’s disease) Aflatoxin exposure (mold-contaminated grains and nuts) Older age Symptoms Early HCC usually has no noticeable symptoms. When symptoms appear, the disease is often advanced and may include: Unintentional weight loss Loss of appetite Upper abdominal pain or mass Abdominal swelling Jaundice (yellowing of skin and eyes) Worsening symptoms of cirrhosis Early warning signs may be detected through: Rising alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) levels New liver nodules on ultrasound during surveillance How HCC spreads Advanced HCC may spread to: Lungs Abdominal lymph nodes Bones Adrenal glands Brain Treatment options Treatment depends on tumor stage and liver function and may include: Surgical resection Liver transplantation Ablation therapies Embolization (TACE, TARE) Radiation therapy Targeted therapy Immunotherapy Prevention You can reduce the risk of HCC by: Preventing or treating hepatitis B and C Getting vaccinated against hepatitis B Avoiding heavy alcohol use Maintaining a healthy weight Managing diabetes and metabolic disease Avoiding smoking Treating cirrhosis early Screening People at high risk (cirrhosis, hepatitis B or C) may benefit from screening every 6 months with: Liver ultrasound AFP blood test Screening can detect HCC earlier, when treatment is more effective. When to see a doctor See a healthcare professional if you have: New or worsening liver-related symptoms Unexplained weight loss or abdominal pain Known liver disease and changes in health status Early detection is critical for improving outcomes in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Patients served
Countries
Clinics
Experienced doctors
Your Benefits and Guarantees with Amedical
Experience a seamless and secure breast lift journey with Amedical.Transparent Prices and Flexible Installment Plans
No hidden fees — only official clinic prices. You can pay for your breast lift directly at the clinic upon arrival and use a flexible installment plan if needed.
Verified Clinics and Doctors Only
Amedical is fully committed to your safety. We cooperate exclusively with medical institutions that meet high international standards in breast lift procedures and are licensed to serve international patients.
Free 24/7 Support Service
Amedical provides free expert assistance. Your personal medical coordinator supports you before, during, and after your treatment, helping to resolve any issues. You are never alone on your breast lift journey.

Your personal AMedical medical coordinator
Supports you at every stage
Helps choose the right clinic and doctor
Ensures quick and convenient access to information
Loading clinics...
Our Trusted Doctors
Our doctors are highly skilled and experts in their fields.

Orthopaedic surgeon and pediatric traumatologist Languages: English, Spanish, Catalan, Portuguese

Orthopaedic surgeon and pediatric traumatologist Languages: English, Spanish and Catalan

Paediatric surgeon Languages: Spanish, Catalan, English and French
Related Articles
Stay informed with our latest medical insights and health tips

Best Countries for Insomnia Treatment Abroad
Many people search for the best countries for insomnia treatment or the best and cheapest countries for insomnia treatment to find trusted clinics with proven results.

Azerbaijan: A Hidden Gem for Medical Tourism
Azerbaijan has a well-developed healthcare system that provides a wide range of medical services to its citizens.
Gamma Knife Surgery in Turkey - Costs, Best Clinics & Doctors
This article discusses the details of Gamma Knife surgery in Turkey, including the cost, procedure, and recommendations for clinics and doctors.
Country Treatment
Find the best treatment options available in your country.
Get a free consultation
Talk to our experts and discover the best solution for your needs completely free of charge.
