Treatment Abroad – Find Verified Clinics, Reviews & Prices
Treatment Abroad made simple by A-Medical. Explore top clinics worldwide and start your journey toward better health today
We make healthcare abroad
simple, transparent, and fully guided from start to finish
Submit Your Request
Tell us about your treatment needs. We carefully review your case and match you with the most suitable hospitals and doctors.
Get Official Price Quotes
We provide verified treatment offers and proformas directly from hospitals — no middlemen, full transparency.
Connect with Doctors
We arrange direct calls or video consultations with hospitals and doctors so you can discuss your treatment plan confidently.
Confirm & Start Treatment
Once you accept the treatment plan, we schedule your hospital appointment and support you throughout your medical journey.
Clinics
Discover our network of world-class medical facilities offering comprehensive healthcare services
Why Choose Us
With us, you are in safe hands. We focus on quality, transparency, and patient-first care. Here’s what sets us apart
Only Accredited Hospitals
We partner exclusively with internationally accredited and top-ranked hospitals.
Direct & Transparent Payments
You pay directly at the hospital, with no hidden fees.
Free Direct Call & Video Consultation
Speak with our experts and doctors before making any decisions.
Best Doctor & Hospital Match
We carefully select the most suitable specialist and clinic for your treatment needs.
Worldwide Hospital Network
Access to a vast global network across 90+ countries.
More Affordable Pricing
We negotiate better prices from hospitals than you would get by contacting them directly.
Medical Conditions
Explore our comprehensive coverage of medical conditions and find the right treatment options
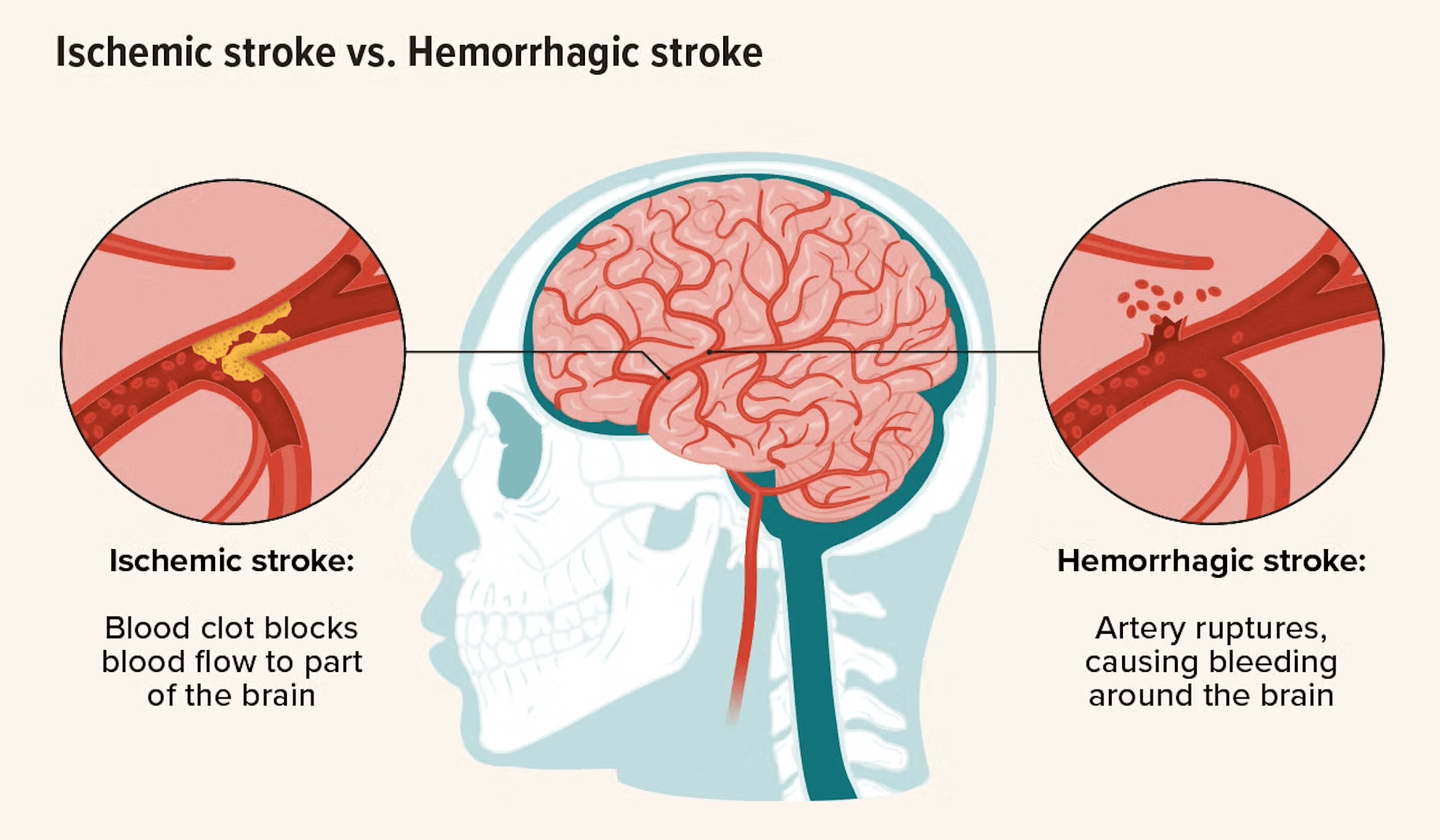
Ischaemic stroke
What is an ischaemic stroke? An ischaemic stroke, also called a cerebral infarction, happens when a blood clot or other obstruction blocks an artery supplying blood to the brain. This blockage sharply reduces blood flow, depriving brain tissue of oxygen and nutrients. Without oxygen, brain cells begin to die within minutes. Ischaemic strokes are the most common type of stroke, accounting for around 80% of all cases, and they are a medical emergency. Rapid treatment is critical to limit brain damage, disability, and life-threatening complications. Types of ischaemic stroke 1. Thrombotic stroke Caused by a blood clot (thrombus) that forms directly in an artery supplying the brain Commonly linked to atherosclerosis, where fatty plaques narrow the arteries Often develops during sleep or rest 2. Embolic stroke Occurs when a clot forms elsewhere in the body, most often in the heart The clot travels through the bloodstream and becomes lodged in a brain artery Frequently associated with atrial fibrillation, heart valve disease, or recent heart attack 3. Lacunar stroke Involves blockage of small, deep arteries within the brain Usually caused by long-standing high blood pressure leading to thickened vessel walls Can also be linked to diabetes or rare genetic conditions Symptoms of an ischaemic stroke Symptoms depend on which area of the brain is affected, but commonly include: Sudden numbness or weakness, especially on one side of the face, arm, or leg Sudden difficulty speaking or understanding speech Sudden vision problems in one or both eyes Sudden dizziness, loss of balance, or difficulty walking Sudden severe headache with no known cause When to seek emergency medical attention – ACT FAST Call emergency services immediately if you notice: F – Face drooping when smiling A – Arm weakness when raising one or both arms S – Speech difficulty or slurred speech T – Time to call emergency services Early treatment can be lifesaving and can significantly reduce long-term disability. What causes an ischaemic stroke? Several conditions can lead to artery blockage, including: Atherosclerosis (plaque build-up in arteries) Blood clots from the heart, often due to atrial fibrillation or heart valve disease High blood pressure, which damages and narrows blood vessels Carotid artery disease, causing reduced blood flow to the brain Blood disorders, such as sickle cell disease or clotting abnormalities Inflammatory or genetic blood vessel diseases Complications and related conditions An ischaemic stroke can cause long-term or permanent complications, such as: Paralysis or weakness, usually on one side of the body Speech and swallowing difficulties (dysphagia) Memory, concentration, and cognitive problems Chronic pain, numbness, or abnormal sensations Depression, anxiety, and emotional changes Secondary issues including pneumonia, pressure sores, or deep vein thrombosis due to reduced mobility How can ischaemic strokes be prevented? Prevention focuses on controlling risk factors and maintaining vascular health: Control blood pressure, diabetes, and cholesterol Eat a balanced, heart-healthy diet low in saturated fat and salt Exercise regularly Stop smoking and limit alcohol intake Take prescribed medications for heart rhythm disorders or clot prevention Attend regular health check-ups to monitor stroke risk factors
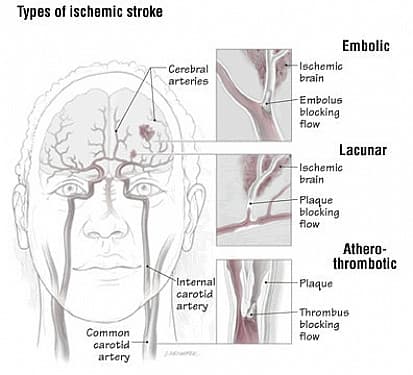
Lacunar syndromes
Lacunar Syndromes – Clear Clinical Overview Lacunar syndromes are a group of distinct neurological presentations caused by small deep infarcts (lacunes) in the brain. These infarcts result from occlusion of small penetrating arteries, most commonly due to chronic hypertension, but also diabetes and smoking. Unlike large strokes, lacunar strokes do not involve the cerebral cortex, which explains their characteristic pattern of symptoms. The Five Classical Lacunar Syndromes 1. Pure Motor Stroke (Pure Motor Hemiparesis) Most common lacunar syndrome Weakness or paralysis of the face, arm, and leg on one side No sensory loss Common lesion sites: Posterior limb of the internal capsule Basis pontis 2. Pure Sensory Stroke Numbness, tingling, or altered sensation on one side of the body No motor weakness Typically involves the thalamus (especially the ventral posterolateral nucleus) 3. Ataxic Hemiparesis Combination of: Ipsilateral weakness Poor coordination (ataxia), especially affecting gait Often appears as “clumsy walking” Common lesion sites: Pons Internal capsule Corona radiata 4. Dysarthria–Clumsy Hand Syndrome Slurred speech (dysarthria) Clumsiness and poor fine motor control of the hand Facial weakness may be present Lesions usually located in: Pons Internal capsule 5. Mixed Sensorimotor Stroke Motor weakness and sensory loss on the same side of the body Often due to lesions involving both: Thalamus (sensory) Internal capsule (motor) Causes & Pathophysiology Lacunar strokes result from disease of small penetrating arteries: 🔹 Main mechanisms Occlusion of a single small artery Lipohyalinosis Vessel wall thickening and degeneration from chronic hypertension Microatheroma Small atherosclerotic plaque within the penetrating artery 🔹 Resulting lesion Lacune: A small, fluid-filled cavity in brain tissue Size: 3–15 mm Common Brain Locations Involved Internal capsule Thalamus Pons Basal ganglia Corona radiata These are deep brain structures, which explains the symptom pattern. Diagnosis & Key Clinical Characteristics Diagnosis Clinical syndrome recognition is essential MRI (especially DWI) confirms diagnosis by showing a small deep infarct Key distinguishing features ✅ Deficits confined to motor and/or sensory pathways ❌ No cortical signs, such as: Aphasia Neglect Visual field loss Seizures This absence of cortical features helps differentiate lacunar syndromes from larger territorial strokes. Clinical Importance Lacunar strokes often have better short-term survival, but: Recurrent lacunes can lead to vascular dementia Associated with chronic small vessel disease Strongly linked to long-standing uncontrolled hypertension
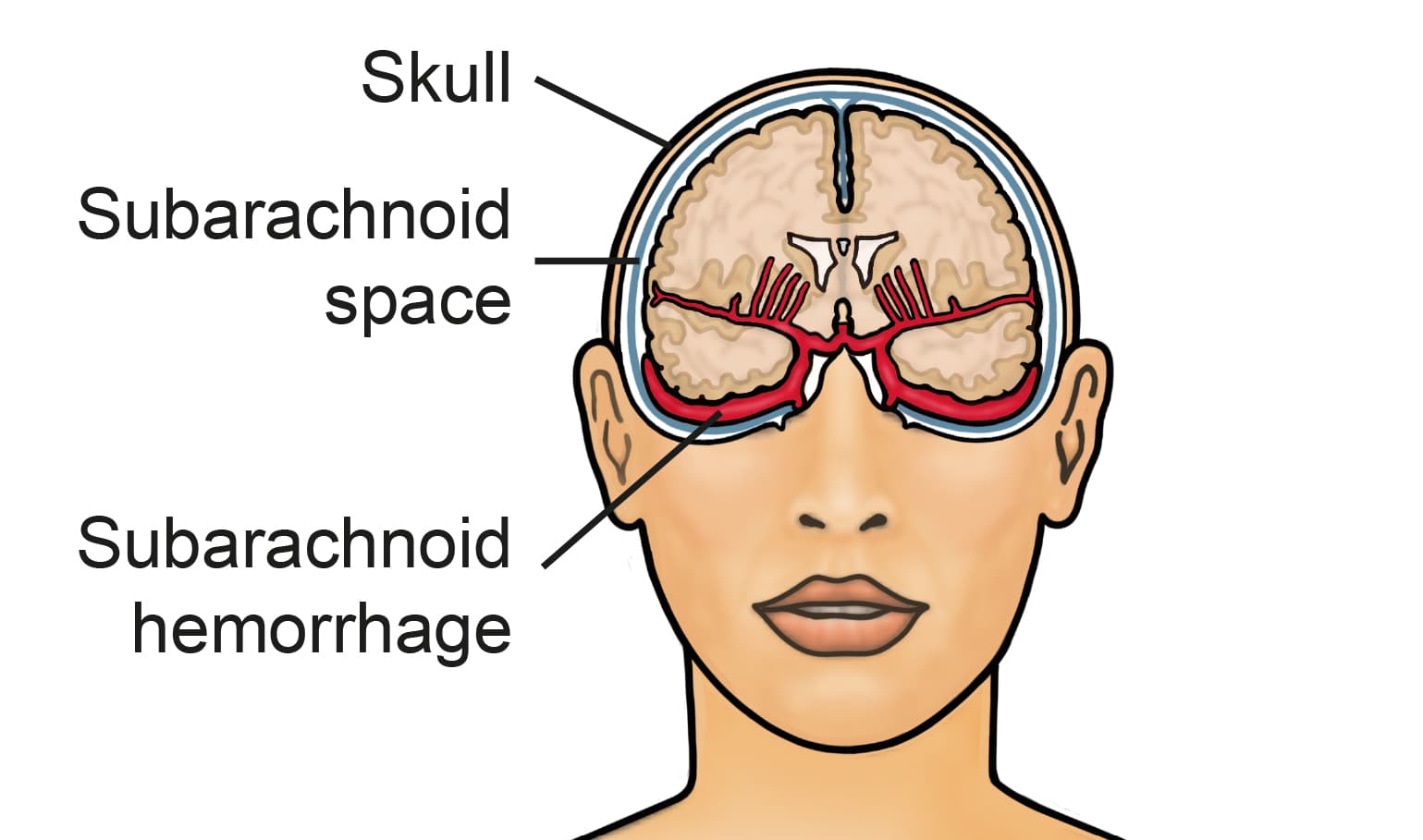
Subarachnoid Haemorrhage
What Is a Subarachnoid Haemorrhage? A subarachnoid haemorrhage (SAH) is a serious and potentially life-threatening type of haemorrhagic stroke. It occurs when bleeding develops in the subarachnoid space—the area between the brain and the thin protective membranes (meninges) that cover it. This space normally contains cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), which cushions and protects the brain and spinal cord. When bleeding occurs in this area, it can rapidly increase pressure inside the skull, damage brain tissue, and disrupt normal brain function. Subarachnoid haemorrhage is a medical emergency and requires immediate diagnosis and treatment. Difference Between Subarachnoid Haemorrhage and Subdural Haematoma Although both conditions involve bleeding inside the skull, they occur in different locations: Subarachnoid haemorrhage (SAH): Bleeding occurs in the subarachnoid space, between the brain and the membranes covering it. Subdural haematoma: Bleeding occurs between the dura mater (the outermost membrane) and the arachnoid membrane. These differences are important because they affect symptoms, causes, and treatment approaches. Symptoms of Subarachnoid Haemorrhage Symptoms usually appear suddenly and are often severe. Common signs include: Sudden, intense headache often described as a “thunderclap headache” Nausea and vomiting Stiff neck due to irritation of the meninges Sensitivity to light (photophobia) Blurred or double vision Loss of consciousness, ranging from brief fainting to coma Seizures Confusion, disorientation, or difficulty thinking clearly Any sudden severe headache should be treated as a medical emergency. Causes of Subarachnoid Haemorrhage Primary Causes Ruptured cerebral aneurysm: The most common cause; occurs when a weakened blood vessel bulges and bursts Head trauma: Due to falls, road traffic accidents, or direct blows to the head Arteriovenous malformations (AVMs): Abnormal tangles of blood vessels that are prone to rupture Contributing Risk Factors Blood clotting disorders Use of blood-thinning medications Chronic high blood pressure (hypertension), which weakens blood vessels over time Complications and Related Conditions Subarachnoid haemorrhage can result in severe short- and long-term complications, including: Re-bleeding, particularly in the early period after the initial haemorrhage Cerebral vasospasm, where brain blood vessels narrow and restrict blood flow Hydrocephalus, an accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid that may require surgical drainage Seizure disorders Long-term disability, including paralysis, speech difficulties, memory loss, and emotional or behavioural changes The severity of complications depends on the extent and location of the bleeding and how quickly treatment is initiated. How Can Subarachnoid Haemorrhage Be Prevented? While not all cases are preventable, reducing risk factors can significantly lower the likelihood of a subarachnoid haemorrhage: Regular monitoring and control of high blood pressure Maintaining a healthy, balanced diet low in saturated and trans fats Engaging in regular physical activity Avoiding smoking and limiting alcohol consumption Proper management of chronic conditions such as diabetes and heart disease Routine medical check-ups and screenings, especially for individuals with a family history of aneurysms
Get a free consultation
Talk to our experts and discover the best solution for your needs completely free of charge.

Related Articles
Stay informed with our latest medical insights and health tips
Leykosit Nədir? Qanda Leykosit Azlığı və Çoxluğu Səbəbləri
Ağ qan hüceyrələri, insan bədənindəki müdafiə sistemini idarə edən hüceyrə qrupudur. Qan dövranında hərəkət edərək orqanizmi virus, bakteriya və digər yad strukturlardan qoruyurlar.

Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Treatment in Turkey
Access world-class Multiple Sclerosis treatment in Turkey with up to 60% savings. Our 2026 guide details advanced therapies like Stem Cell and DBS, top JCI-accredited hospitals, and all-inclusive pack...
Robotic Hair Transplant in Istanbul, Turkey
Contact us to get robotic hair transplant in Turkey with the participation of highly qualified clinics and specialist doctors.
Our doctor is highly skilled and an expert in their field.









