Treatment Abroad – Find Verified Clinics, Reviews & Prices
Treatment Abroad made simple by A-Medical. Explore top clinics worldwide and start your journey toward better health today
We make healthcare abroad
simple, transparent, and fully guided from start to finish
Submit Your Request
Tell us about your treatment needs. We carefully review your case and match you with the most suitable hospitals and doctors.
Get Official Price Quotes
We provide verified treatment offers and proformas directly from hospitals — no middlemen, full transparency.
Connect with Doctors
We arrange direct calls or video consultations with hospitals and doctors so you can discuss your treatment plan confidently.
Confirm & Start Treatment
Once you accept the treatment plan, we schedule your hospital appointment and support you throughout your medical journey.
Clinics
Discover our network of world-class medical facilities offering comprehensive healthcare services
Why Choose Us
With us, you are in safe hands. We focus on quality, transparency, and patient-first care. Here’s what sets us apart
Only Accredited Hospitals
We partner exclusively with internationally accredited and top-ranked hospitals.
Direct & Transparent Payments
You pay directly at the hospital, with no hidden fees.
Free Direct Call & Video Consultation
Speak with our experts and doctors before making any decisions.
Best Doctor & Hospital Match
We carefully select the most suitable specialist and clinic for your treatment needs.
Worldwide Hospital Network
Access to a vast global network across 90+ countries.
More Affordable Pricing
We negotiate better prices from hospitals than you would get by contacting them directly.
Medical Conditions
Explore our comprehensive coverage of medical conditions and find the right treatment options
Hip replacement
Hip replacement
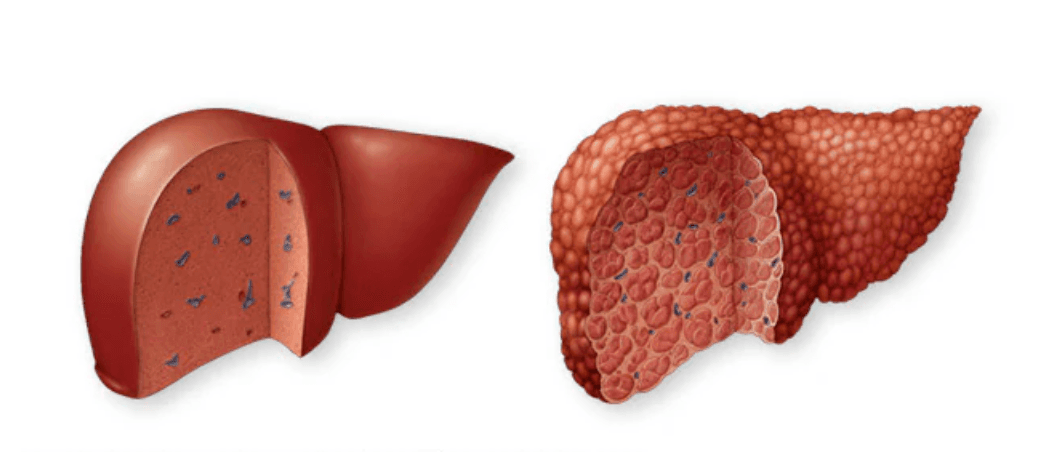
Toxic hepatitis
Toxic hepatitis is inflammation of the liver caused by exposure to harmful substances, such as alcohol, medications, chemicals, or herbal/nutritional supplements. It may develop within hours or days after exposure, or after months of repeated contact. Symptoms often improve once the toxin is stopped, but severe cases can lead to cirrhosis or life-threatening liver failure. Symptoms Mild cases may have no symptoms and are found on blood tests. When present, symptoms include: Jaundice (yellowing of skin/eyes) Itching Pain in the upper right abdomen Fatigue Loss of appetite Nausea and vomiting Fever or rash Weight loss Dark (tea-colored) urine Emergency: Suspected acetaminophen (paracetamol) overdose requires immediate medical care—do not wait for symptoms. Causes Alcohol (long-term heavy use) Over-the-counter pain relievers (acetaminophen, aspirin, ibuprofen, naproxen), especially in high doses or with alcohol Prescription drugs (e.g., statins, certain antibiotics, antivirals, steroids) Herbs & supplements (e.g., aloe vera, black cohosh, kava, ephedra) Industrial chemicals (e.g., carbon tetrachloride, vinyl chloride, paraquat) The liver breaks down toxins, but byproducts can damage liver cells—repeated exposure increases harm. Risk Factors Existing liver disease or viral hepatitis Older age Female sex (slower toxin metabolism for some substances) Certain genetic enzyme differences Complications Cirrhosis (permanent scarring) Acute or chronic liver failure Liver transplant may be required in severe cases Prevention Use medicines only as directed; avoid unnecessary use Never mix alcohol with acetaminophen; ask about other drugs Be cautious with herbs/supplements—discuss risks with a professional Use protective measures when handling chemicals Keep medicines and chemicals out of children’s reach Bottom line: Toxic hepatitis is often preventable. Early recognition and stopping the offending substance can protect the liver and prevent serious complications.
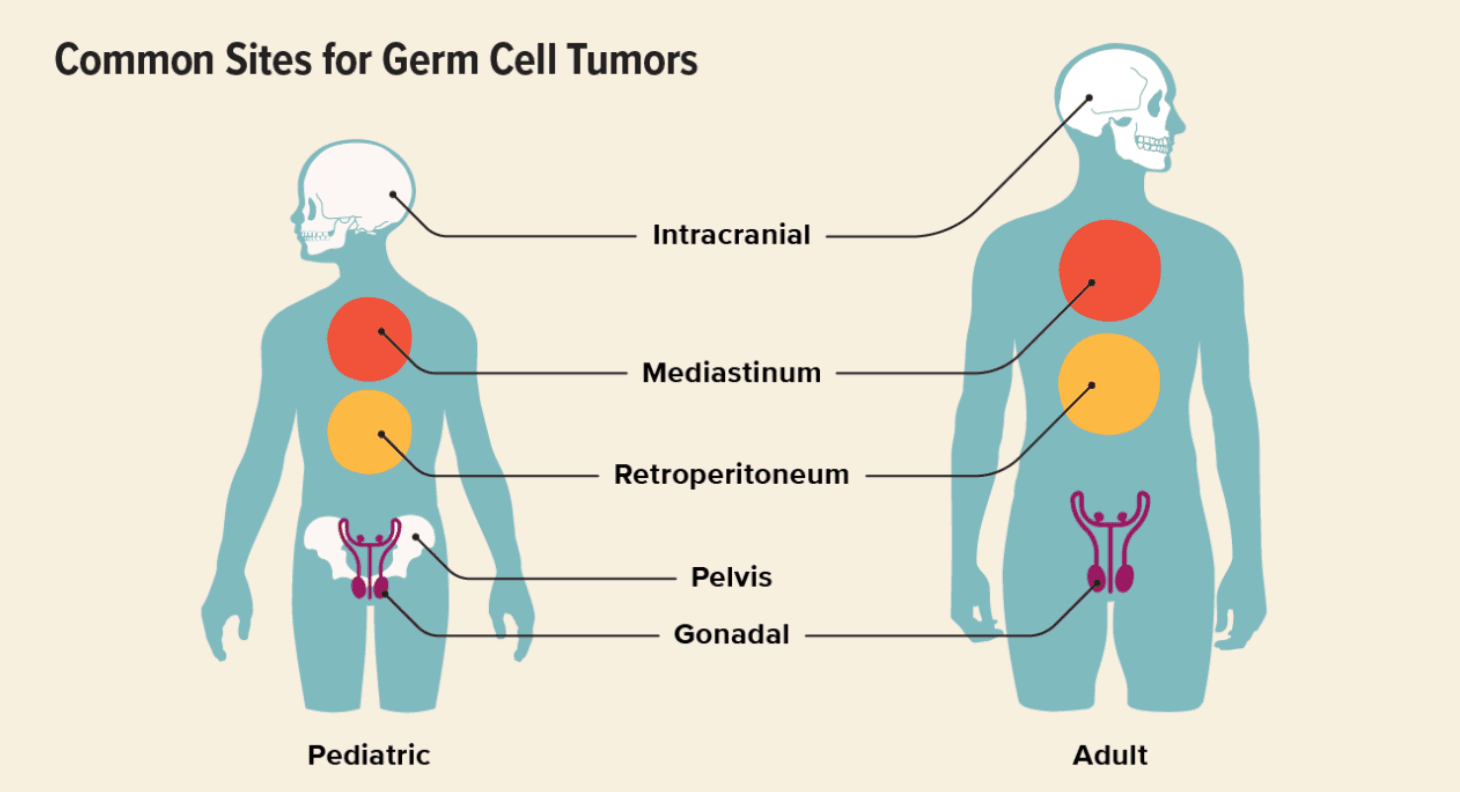
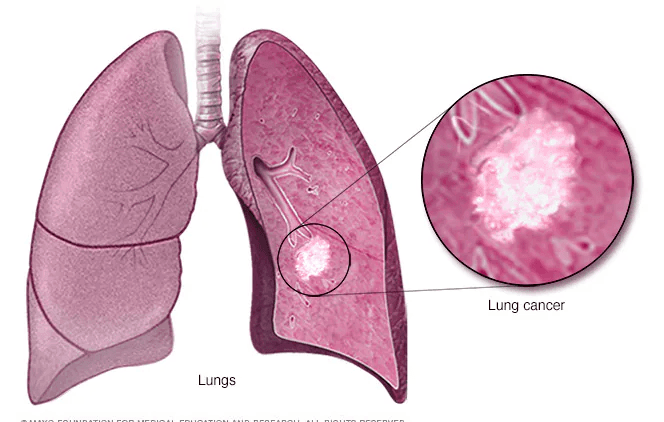
Germ Cell Tumor
Germ cells, also called gametes, are specialized cells responsible for sexual reproduction. Their name comes from the word germinate, meaning “to begin to grow.” During fetal development, germ cells migrate to specific locations and later develop into sperm in males or egg cells (ova) in females. In some cases, germ cells undergo abnormal growth and form a germ cell tumor (GCT). These tumors most commonly develop in the testicles or ovaries, but in rare cases, they can appear in other parts of the body. Germ cell tumors are rare and most often occur in adolescents and young adults between ages 15 and 30, though they can affect children and older adults as well. Types of Germ Cell Tumors Germ cell tumors can be classified by behavior, sex, and location. By Behavior Benign (non-cancerous) Malignant (cancerous) By Sex In males (testicular germ cell tumors): Seminoma Non-seminoma In females (ovarian germ cell tumors): Dysgerminoma Non-dysgerminoma Other Germ Cell Tumor Types Teratoma (benign or malignant) Choriocarcinoma Germinoma Embryonal carcinoma Endodermal sinus tumor (yolk sac tumor) Polyembryoma Mixed germ cell tumors Extragonadal Germ Cell Tumors In rare cases, germ cell tumors develop outside the ovaries or testicles. These are called extragonadal germ cell tumors and may appear in: Mediastinum (chest) Pineal region of the brain Retroperitoneum (back of the abdomen) Sacrococcygeal area (base of the spine) Causes and Risk Factors The exact cause of germ cell tumors is not fully understood, but several factors increase risk: Genetic syndromes (e.g., Turner syndrome, Klinefelter syndrome) Birth defects involving the genitals, spine, or urinary tract Cryptorchidism (undescended testicle) Age, especially males aged 15–35 and adolescent girls or young women Germ Cell Tumor Symptoms Symptoms depend on the tumor’s type and location. Ovarian Germ Cell Tumors Abdominal swelling Pelvic pain Constipation Irregular vaginal bleeding Testicular Germ Cell Tumors Testicular lump or swelling Groin pain Heaviness in the scrotum Extragonadal Germ Cell Tumors Breathing difficulty (mediastinal tumors) Urinary problems Leg weakness or neurological symptoms (spinal involvement) Diagnosis Early detection is critical. Diagnostic tests may include: Physical examination Imaging tests (ultrasound, CT scan, MRI) Blood tests (tumor markers such as AFP, β-hCG, LDH) Biopsy or surgical removal for definitive diagnosis Germ Cell Tumor Staging Staging determines how far the tumor has spread and guides treatment. Stage 1 Tumor confined to the original site Often treated with surgery alone Stage 2 Spread to nearby tissues or structures Still localized to the pelvic or regional area Stage 3 Spread to distant areas or regional lymph nodes Stage 4 Metastasis to distant organs Common sites: lungs, liver, distant lymph nodes Germ Cell Tumor Treatment Treatment is individualized based on tumor type, stage, and patient factors. Surgery First-line treatment for localized tumors May involve removal of the tumor and, if necessary, the affected ovary or testicle Fertility-sparing surgery is often possible Chemotherapy Highly effective because germ cell tumors are very chemo-sensitive Used for advanced, aggressive, or metastatic disease Radiotherapy may be added in select cases Immunotherapy Used in relapsed or chemotherapy-resistant tumors Helps the immune system target cancer cells Prognosis Germ cell tumors generally have an excellent prognosis, especially when diagnosed early. Testicular germ cell tumors: ~95% survival rate Ovarian germ cell tumors: ~93% survival rate Outcomes depend on tumor location, stage at diagnosis, response to treatment, and overall patient health.
Get a free consultation
Talk to our experts and discover the best solution for your needs completely free of charge.

Related Articles
Stay informed with our latest medical insights and health tips

Best Stem Cell Therapy Clinics in Georgia
Georgia advances as a leading center for regenerative medicine, cellular therapy, and advanced biologics due to regulated clinical frameworks, laboratory-controlled cell processing, and internationall...
All-Inclusive Tummy Tuck in Turkey: Costs, Clinics, Packages
Tummy Tuck in Turkey has become one of the most frequently chosen procedures by international patients traveling abroad for cosmetic surgery.
Kidney Transplant in Turkey
Kidney transplantation is the process of replacing a damaged or diseased kidney with a healthy kidney from a healthy donor.
Our doctor is highly skilled and an expert in their field.









