Treatment Abroad – Find Verified Clinics, Reviews & Prices
Treatment Abroad made simple by A-Medical. Explore top clinics worldwide and start your journey toward better health today
We make healthcare abroad
simple, transparent, and fully guided from start to finish
Submit Your Request
Tell us about your treatment needs. We carefully review your case and match you with the most suitable hospitals and doctors.
Get Official Price Quotes
We provide verified treatment offers and proformas directly from hospitals — no middlemen, full transparency.
Connect with Doctors
We arrange direct calls or video consultations with hospitals and doctors so you can discuss your treatment plan confidently.
Confirm & Start Treatment
Once you accept the treatment plan, we schedule your hospital appointment and support you throughout your medical journey.
Clinics
Discover our network of world-class medical facilities offering comprehensive healthcare services
Why Choose Us
With us, you are in safe hands. We focus on quality, transparency, and patient-first care. Here’s what sets us apart
Only Accredited Hospitals
We partner exclusively with internationally accredited and top-ranked hospitals.
Direct & Transparent Payments
You pay directly at the hospital, with no hidden fees.
Free Direct Call & Video Consultation
Speak with our experts and doctors before making any decisions.
Best Doctor & Hospital Match
We carefully select the most suitable specialist and clinic for your treatment needs.
Worldwide Hospital Network
Access to a vast global network across 90+ countries.
More Affordable Pricing
We negotiate better prices from hospitals than you would get by contacting them directly.
Medical Conditions
Explore our comprehensive coverage of medical conditions and find the right treatment options

Lymphoma
This includes both Hodgkin’s and non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas
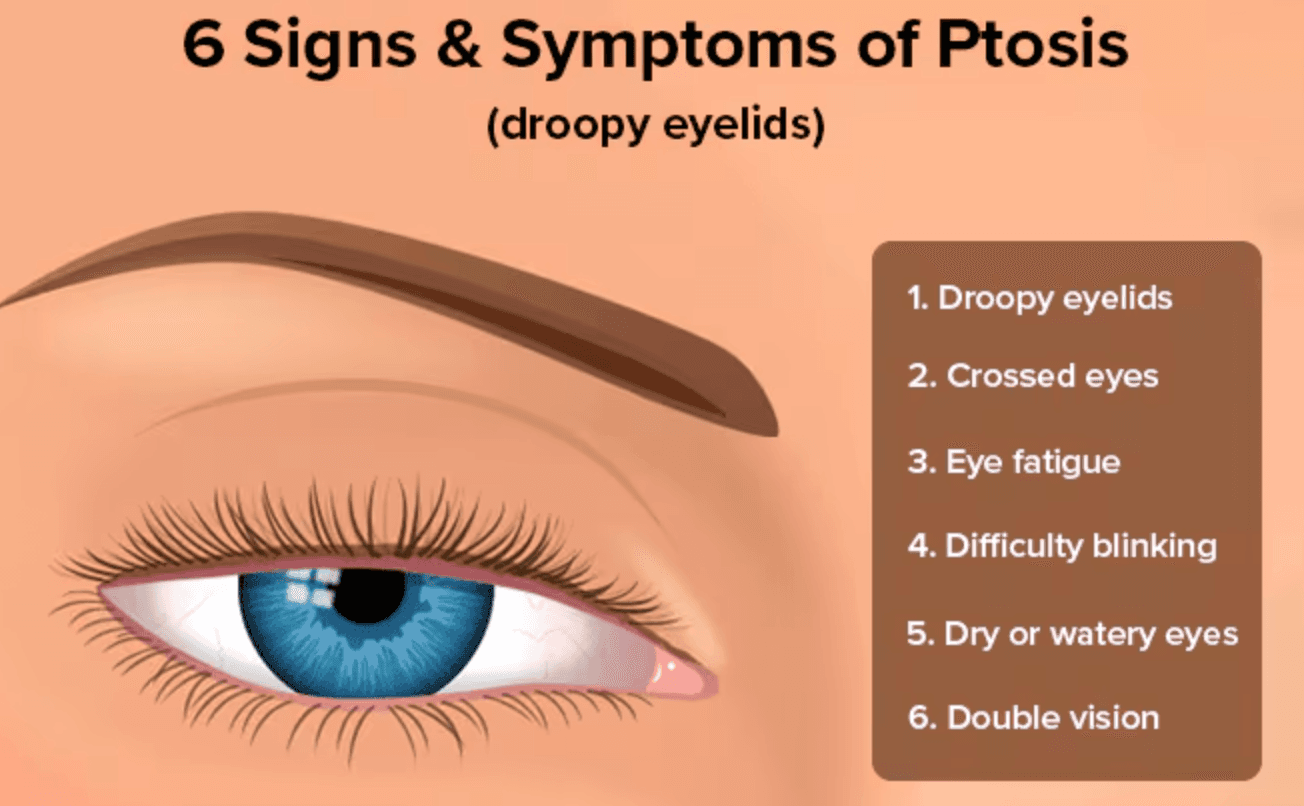
Ptosis (Droopy Eyelid)
Ptosis (Droopy Eyelid)
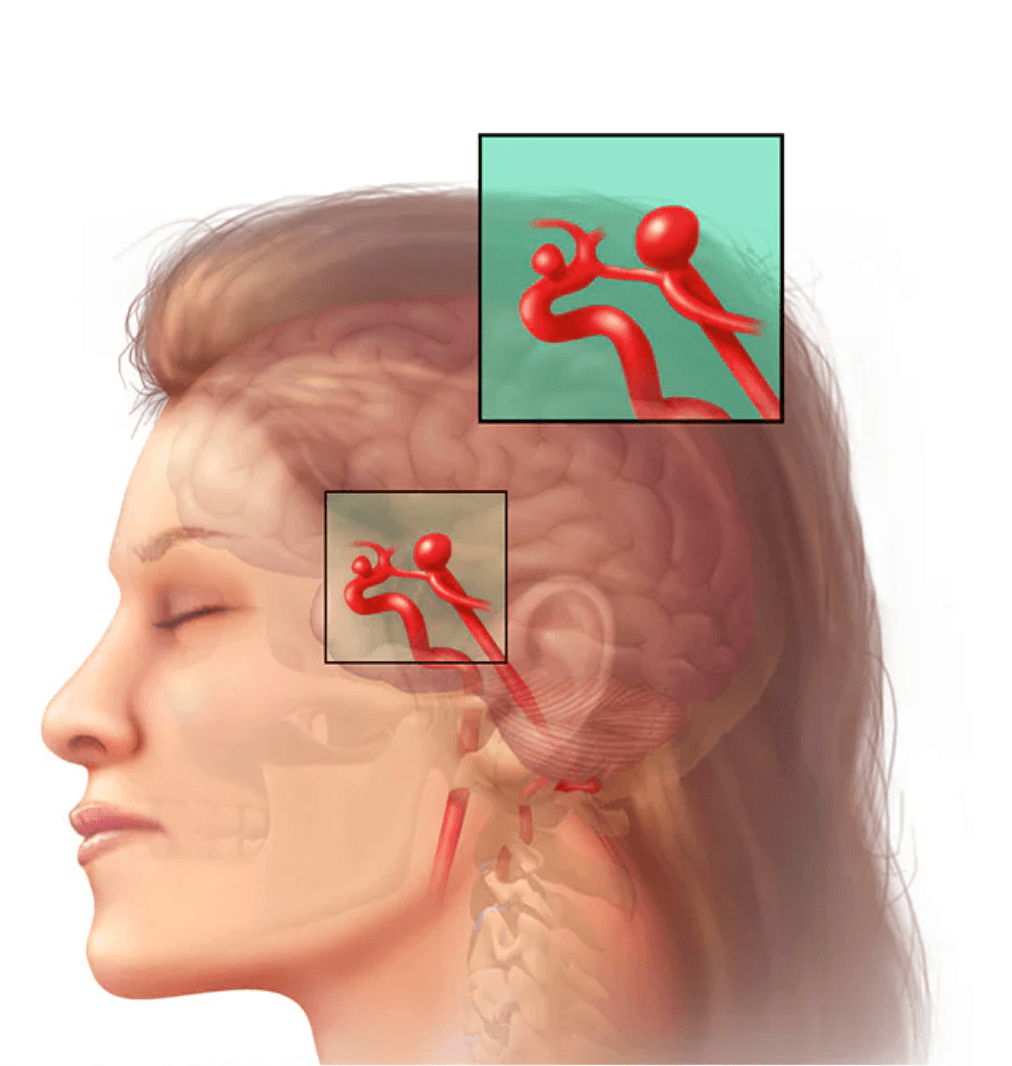
Brain aneurysm
What Is a Brain Aneurysm? A brain aneurysm, also called a cerebral aneurysm, is a bulge or balloon-like swelling that forms in a weakened area of an artery in the brain. Over time, pressure from blood flow can cause this weakened section of the vessel wall to expand. Brain aneurysms vary in size and risk. Many never cause symptoms, while others can rupture and become life-threatening. Types of Brain Aneurysms Unruptured Brain Aneurysm Most brain aneurysms do not rupture. Many remain undetected for years and cause no symptoms unless they grow large enough to press on nearby nerves or brain tissue. Ruptured Brain Aneurysm In a smaller number of cases, an aneurysm can rupture, leading to bleeding in the brain (hemorrhagic stroke). This is a medical emergency and can result in permanent brain damage or death. The risk of rupture is higher in women and people over 40 years of age. Symptoms of a Brain Aneurysm Symptoms of an Unruptured Brain Aneurysm Most unruptured aneurysms cause no symptoms. However, if an aneurysm enlarges and compresses nearby structures, symptoms may include: Sudden changes in vision (blurred, double vision, or vision loss) Pain above or behind one eye Dilated pupil(s) Drooping eyelid Weakness or paralysis on one side of the face Difficulty speaking Symptoms of a Ruptured Brain Aneurysm The hallmark symptom of a ruptured aneurysm is a sudden, severe headache, often described as the “worst headache of my life” (also known as a thunderclap headache). Other symptoms may include: Nausea and vomiting Sensitivity to light Neck stiffness or pain Seizures Confusion or disorientation Loss of consciousness or brief blackouts 🚨 Seek immediate medical attention if these symptoms occur. A persistent headache lasting days or weeks may also indicate a leaking aneurysm and should be urgently evaluated. What Causes a Brain Aneurysm? Brain aneurysms develop due to a weakened or defective artery wall, although the exact cause is not always known. Contributing factors may include: Degenerative changes related to aging High blood pressure Atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries due to fatty deposits) Aneurysms most commonly form in large arteries at the base of the brain or at branching points where vessel walls are naturally weaker. Risk Factors for Brain Aneurysms Several factors increase the likelihood of developing a brain aneurysm: Family history (especially first-degree relatives) Genetic connective tissue disorders, such as Ehlers-Danlos syndrome or Marfan syndrome Congenital conditions, including polycystic kidney disease, arteriovenous malformations (AVMs), and coarctation of the aorta High blood pressure (hypertension) Smoking Excessive alcohol consumption Drug use, particularly cocaine Severe head injury Certain infections (rare, but can cause mycotic aneurysms) Increasing age, especially over 40 Female gender Complications and Related Conditions An unruptured aneurysm can increase pressure inside the skull. If rupture occurs, bleeding disrupts normal blood flow and oxygen delivery to the brain, potentially leading to: Hemorrhagic stroke Permanent brain damage Coma Death Other serious complications include: Re-bleeding, causing further brain injury Vasospasm, narrowing blood vessels and increasing stroke risk Hydrocephalus, a buildup of cerebrospinal fluid causing pressure on the brain Hyponatremia, dangerous sodium imbalance leading to brain swelling Seizures, due to electrical disturbances in the brain Can Brain Aneurysms Be Prevented? There is no guaranteed way to prevent brain aneurysms. However, the risk can be reduced through healthy lifestyle choices: Quit smoking Avoid recreational drugs Control high blood pressure Limit alcohol and caffeine intake Maintain a balanced, low-salt diet Exercise regularly Maintain a healthy weight
Get a free consultation
Talk to our experts and discover the best solution for your needs completely free of charge.

Related Articles
Stay informed with our latest medical insights and health tips

Alternatives to Stem Cell Therapy for Autism
Autism treatment does not follow a single path. While stem cell therapy attracts global attention, many families achieve meaningful progress through evidence-based alternatives like ABA, speech therap...
Thalassemia Treatment in Turkey (Costs, Best Doctors & Clinics)
Thalassemia treatment in Turkey has shown notable success over the years. The condition, commonly known as Mediterranean anemia, is a genetic blood disorder affecting hemoglobin production in red bloo...
Best Countries in the World for Liver Transplant
Liver transplantation is a highly complex medical procedure requiring advanced facilities, experienced surgeons, and comprehensive patient care.
Our doctor is highly skilled and an expert in their field.









