Treatment Abroad – Find Verified Clinics, Reviews & Prices
Treatment Abroad made simple by A-Medical. Explore top clinics worldwide and start your journey toward better health today
We make healthcare abroad
simple, transparent, and fully guided from start to finish
Submit Your Request
Tell us about your treatment needs. We carefully review your case and match you with the most suitable hospitals and doctors.
Get Official Price Quotes
We provide verified treatment offers and proformas directly from hospitals — no middlemen, full transparency.
Connect with Doctors
We arrange direct calls or video consultations with hospitals and doctors so you can discuss your treatment plan confidently.
Confirm & Start Treatment
Once you accept the treatment plan, we schedule your hospital appointment and support you throughout your medical journey.
Clinics
Discover our network of world-class medical facilities offering comprehensive healthcare services
Why Choose Us
With us, you are in safe hands. We focus on quality, transparency, and patient-first care. Here’s what sets us apart
Only Accredited Hospitals
We partner exclusively with internationally accredited and top-ranked hospitals.
Direct & Transparent Payments
You pay directly at the hospital, with no hidden fees.
Free Direct Call & Video Consultation
Speak with our experts and doctors before making any decisions.
Best Doctor & Hospital Match
We carefully select the most suitable specialist and clinic for your treatment needs.
Worldwide Hospital Network
Access to a vast global network across 90+ countries.
More Affordable Pricing
We negotiate better prices from hospitals than you would get by contacting them directly.
Medical Conditions
Explore our comprehensive coverage of medical conditions and find the right treatment options

Glomerulonephritis
A collection of disorders that lead to inflammation and scarring of the kidney’s filtering structures (glomeruli).
Hepatic encephalopathy
Hepatic encephalopathy (HE) is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition that occurs when the liver can no longer remove toxins from the blood, especially ammonia produced in the intestines. When these toxins build up, they impair brain function. Without prompt treatment, HE can progress to coma or death. HE most often develops in people with advanced liver disease, particularly cirrhosis, but it can also occur with acute liver failure, liver cancer, or after certain liver procedures. It affects 30–40% of people with cirrhosis. Alcohol use, infections, medications, internal bleeding, and blood flow abnormalities can trigger episodes. ⚠️ HE is a medical emergency. Sudden confusion, extreme sleepiness, or unresponsiveness requires immediate emergency care. Types of Hepatic Encephalopathy Type A: Caused by acute liver failure, developing rapidly over days or weeks Type B: Caused by abnormal blood flow (portosystemic shunts) that bypasses the liver Type C: Occurs in people with cirrhosis or acute-on-chronic liver failure HE may be: Overt: Symptoms are clearly noticeable Covert: Subtle cognitive changes detectable only with testing Symptoms Difficulty concentrating or confusion Disorientation (not knowing where you are) Daytime sleepiness or insomnia Memory problems Flapping hand tremor (asterixis) Personality or mood changes Slurred speech or poor coordination Coma in severe cases These symptoms can significantly reduce quality of life and daily functioning. Causes and Triggers Liver failure or cirrhosis Alcohol use Infections Gastrointestinal bleeding Electrolyte imbalances (low sodium or potassium) Dehydration or constipation Certain medications (sedatives, opioids, diuretics) Complications after liver transplant Risk Factors Advanced liver disease Diabetes or kidney disease Older age Low muscle mass (sarcopenia) High blood ammonia levels Alcohol use Poor nutrition Possible Complications Falls and injuries Long-term memory and attention problems Driving impairment Frequent hospitalizations Coma Death Prevention You can lower the risk of HE by: Taking medications exactly as prescribed Eating plant-based and dairy protein instead of excessive animal protein Avoiding alcohol, sedatives, and opioids Staying well hydrated Preventing constipation Treating infections promptly Attending regular liver checkups Early recognition and treatment of hepatic encephalopathy can be lifesaving. If you or someone with liver disease develops sudden mental changes, seek emergency medical care immediately.
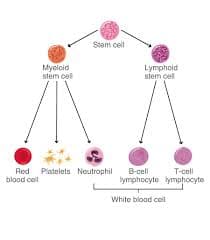
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL)
What Is Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL)? Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is a type of blood cancer that affects the bone marrow and blood. In a healthy body, blood stem cells mature into red blood cells, platelets, and white blood cells (lymphocytes) that help fight infection. In CLL, too many blood stem cells develop into abnormal lymphocytes, also called leukemia cells. These cells do not function properly and cannot fight infections effectively. As they accumulate in the bone marrow and bloodstream, they crowd out healthy blood cells. This can lead to anemia, increased risk of infections, and easy bruising or bleeding. CLL is considered a chronic leukemia, meaning it usually progresses slowly over time. Risk Factors for CLL The main risk factors associated with CLL include: Family history of CLL Family history of cancers of the lymphatic system Age over 70 Male sex White ethnicity Exposure to Agent Orange CLL does not appear to be linked to diet, infections, or smoking. Symptoms of CLL CLL often develops silently. Many people have the disease for years without symptoms and are diagnosed incidentally during routine blood tests for unrelated conditions. When symptoms do appear, they may include: Fatigue and weakness Enlarged lymph nodes (felt as painless lumps under the skin) Abdominal discomfort or a feeling of fullness due to an enlarged spleen Unexplained weight loss Night sweats Frequent or severe infections Types of CLL There are two main biological forms of CLL: Slow-growing (indolent) CLL, which may not require treatment for many years Faster-growing (aggressive) CLL, which progresses more rapidly and requires earlier treatment The difference between these types cannot be determined by symptoms alone. Specialized laboratory and genetic testing are required to identify the form of CLL and guide treatment decisions.
Get a free consultation
Talk to our experts and discover the best solution for your needs completely free of charge.

Related Articles
Stay informed with our latest medical insights and health tips

Best Prostate Cancer Treatment in Switzerland: Top Hospitals & Specialists
Choosing the right path for prostate cancer treatment in Switzerland is a decision driven by more than diagnosis. It involves precision, clarity, and trust.

BBL in Turkey (Brazilian Butt Lift)
Explore the world of Brazilian Buttock (BBL) surgery in Turkey with our guide. By the end, you'll grasp the cost comparisons, procedural insights, and the top clinics specializing in BBL surgery.

Best Countries for Panic Attack and Anxiety Treatment
Choosing the best country for panic attack treatment can be daunting, especially when considering options in foreign countries. A-Medical specializes in taking the stress out of this process by offeri...
Our doctor is highly skilled and an expert in their field.









