Treatment Abroad – Find Verified Clinics, Reviews & Prices
Treatment Abroad made simple by A-Medical. Explore top clinics worldwide and start your journey toward better health today
We make healthcare abroad
simple, transparent, and fully guided from start to finish
Submit Your Request
Tell us about your treatment needs. We carefully review your case and match you with the most suitable hospitals and doctors.
Get Official Price Quotes
We provide verified treatment offers and proformas directly from hospitals — no middlemen, full transparency.
Connect with Doctors
We arrange direct calls or video consultations with hospitals and doctors so you can discuss your treatment plan confidently.
Confirm & Start Treatment
Once you accept the treatment plan, we schedule your hospital appointment and support you throughout your medical journey.
Clinics
Discover our network of world-class medical facilities offering comprehensive healthcare services
Why Choose Us
With us, you are in safe hands. We focus on quality, transparency, and patient-first care. Here’s what sets us apart
Only Accredited Hospitals
We partner exclusively with internationally accredited and top-ranked hospitals.
Direct & Transparent Payments
You pay directly at the hospital, with no hidden fees.
Free Direct Call & Video Consultation
Speak with our experts and doctors before making any decisions.
Best Doctor & Hospital Match
We carefully select the most suitable specialist and clinic for your treatment needs.
Worldwide Hospital Network
Access to a vast global network across 90+ countries.
More Affordable Pricing
We negotiate better prices from hospitals than you would get by contacting them directly.
Medical Conditions
Explore our comprehensive coverage of medical conditions and find the right treatment options
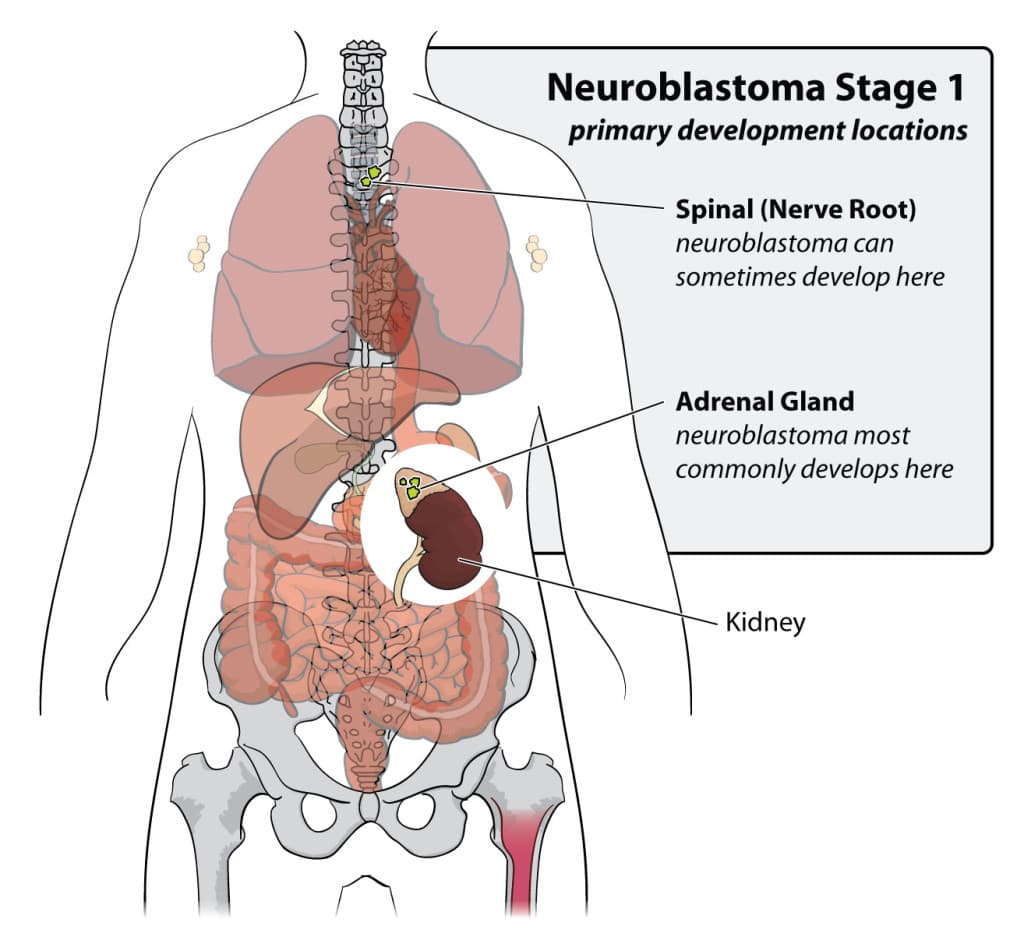
Neuroblastoma
A cancer that arises in specific nerve tissues.
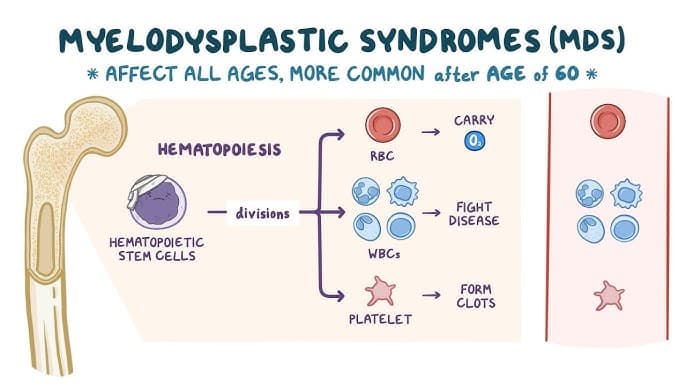
Myelodysplastic Syndromes (MDS)
Myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) are a group of bone marrow disorders in which the marrow fails to produce sufficient healthy blood cells. These conditions arise from mutations in hematopoietic stem cells, leading to ineffective blood formation and the accumulation of immature or abnormal cells. As a result, patients may experience anemia, infections, and bleeding. Although the exact cause of these mutations is often unknown, MDS has been linked to advanced age, genetic predisposition, environmental exposures, and prior chemotherapy or radiation therapy. MDS is considered rare, with an estimated incidence of 4 per 100,000 people annually, though rates are significantly higher in individuals over 60. In some cases, MDS can progress to acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Types of Myelodysplastic Syndromes MDS is classified based on the number of affected blood cell lines, the presence of abnormal cells, and genetic findings: MDS with Single Lineage Dysplasia (MDS-SLD): One blood cell type is dysplastic, usually associated with cytopenia. MDS with Multilineage Dysplasia (MDS-MLD): Two or more blood cell lines are affected, often causing more severe symptoms. MDS with Ring Sideroblasts (MDS-RS): MDS-RS-SLD – ring sideroblasts with single lineage dysplasia MDS-RS-MLD – ring sideroblasts with multilineage dysplasia MDS with Excess Blasts (MDS-EB): MDS-EB1 – 5–9% blasts in blood or 5–10% in marrow MDS-EB2 – 10–19% blasts in blood or 10–20% in marrow MDS with isolated del(5q): Characterized by a chromosome 5 deletion, typically with anemia and normal or elevated platelets. MDS, Unclassifiable (MDS-U): Does not meet criteria for other categories. Each subtype carries a variable risk of progression to AML. Causes and Risk Factors Key risk factors include: Age (most cases occur after 60) Environmental exposures (benzene, pesticides, tobacco smoke) Prior cancer therapy (therapy-related MDS) Inherited bone marrow failure syndromes Rare familial genetic predisposition Lifestyle factors such as smoking and alcohol use Symptoms of MDS Symptoms reflect low or dysfunctional blood cell production: Anemia: fatigue, weakness, shortness of breath, pallor Leukopenia / neutropenia: recurrent or severe infections Thrombocytopenia: easy bruising, bleeding, prolonged clotting Severity ranges from mild to life-threatening and significantly impacts quality of life. Diagnosis Diagnosis requires a comprehensive hematologic evaluation: Complete blood count (CBC) Peripheral blood smear Bone marrow aspiration and biopsy Cytogenetic and molecular genetic testing Flow cytometry for cellular characterization These tests allow accurate classification, prognostication, and treatment planning. Treatment Options Treatment is personalized based on MDS risk level, age, health status, and goals of care. Lower-Risk MDS Supportive care (blood and platelet transfusions) Erythropoiesis-stimulating agents (ESAs) Iron chelation therapy Immunosuppressive therapy in selected cases Higher-Risk MDS Hypomethylating agents (azacitidine, decitabine) Chemotherapy Allogeneic stem cell transplantation (the only curative option) Participation in clinical trials Living with MDS Managing MDS involves addressing both physical and emotional challenges. Regular follow-up, symptom control, nutritional support, and psychological care are essential. Palliative and supportive services play a key role in maintaining quality of life. Expert Care at Sheba Medical Center The Hemato-Oncology Department at Sheba Medical Center specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of myelodysplastic syndromes, offering advanced molecular diagnostics, personalized therapies, and access to innovative clinical trials. Sheba’s multidisciplinary team is committed to delivering state-of-the-art care with compassion, recognizing that every MDS journey is unique.
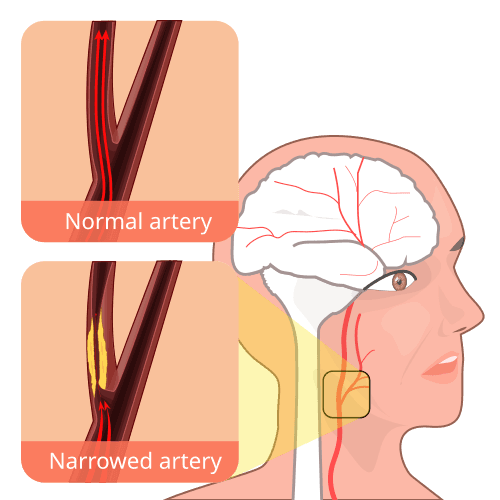
Carotid artery stenosis
What Is Carotid Artery Stenosis? Carotid artery stenosis, also called carotid artery disease, is a condition in which the carotid arteries become narrowed. These arteries run along both sides of the neck and are responsible for supplying oxygen-rich blood to the brain. The narrowing occurs due to the buildup of plaque, a mixture of fat, cholesterol, calcium and other substances found in the blood. Over time, plaque accumulation restricts blood flow to the brain. Carotid artery stenosis is a serious condition because: Severely reduced blood flow can deprive the brain of oxygen A piece of plaque can break off and travel to the brain Blood clots may form and block brain arteries All of these situations can result in a stroke, which can cause permanent disability or death. What Are the Symptoms of Carotid Artery Stenosis? Most people with carotid artery stenosis do not experience symptoms until the artery becomes severely narrowed. In many cases, the first sign of carotid artery stenosis is a stroke or a transient ischemic attack (TIA), often referred to as a “mini-stroke.” A TIA produces stroke-like symptoms, but they: Last only a few minutes Usually resolve within an hour Serve as a serious warning sign of a future stroke Symptoms of Stroke or TIA Seek emergency medical attention immediately if any of the following occur: Sudden numbness or weakness on one side of the face or body Difficulty speaking or slurred speech Dizziness, loss of balance, or trouble walking Sudden vision loss or blurred vision in one or both eyes Severe headache with no known cause What Causes Carotid Artery Stenosis? The primary cause of carotid artery stenosis is atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis is a gradual process in which plaque builds up along the inner walls of the arteries, causing them to: Narrow Harden Lose flexibility As the carotid arteries narrow, less blood reaches the brain. In some cases, plaque can rupture, allowing fragments to travel through the bloodstream and block smaller arteries in the brain, triggering a stroke. Risk Factors for Carotid Artery Stenosis Several factors increase the likelihood of developing carotid artery stenosis: High blood pressure (hypertension) – weakens artery walls Smoking – damages artery lining and raises blood pressure Sedentary lifestyle – increases risk of obesity, diabetes and hypertension High cholesterol levels – promotes plaque formation Diabetes – impairs fat metabolism and accelerates atherosclerosis Obesity – increases risk of cardiovascular disease Advancing age – arteries naturally lose elasticity over time Family history – higher risk if close relatives have atherosclerosis or heart disease Complications and Related Conditions If left untreated, carotid artery stenosis can lead to: Ischemic stroke due to blocked blood flow Transient ischemic attacks (TIAs) Permanent neurological damage Disability Death Stroke is the most serious complication and may result from: Reduced blood flow Plaque rupture Formation of blood clots How Can Carotid Artery Stenosis Be Prevented? Prevention focuses on managing modifiable risk factors through lifestyle and medical interventions: Quit smoking and avoid tobacco products Exercise regularly Maintain a healthy weight Follow a heart-healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables and whole grains Limit salt, saturated fats and processed foods Control blood pressure, cholesterol and blood sugar levels Take prescribed medications as directed Attend regular medical check-ups
Get a free consultation
Talk to our experts and discover the best solution for your needs completely free of charge.

Related Articles
Stay informed with our latest medical insights and health tips

Breast Augmentation (Breast Implants) in Turkey
Planning a breast augmentation in Turkey? Discover a complete, expert-backed guide covering procedures, implant types, pricing, recovery, and why thousands of international patients trust Turkish clin...
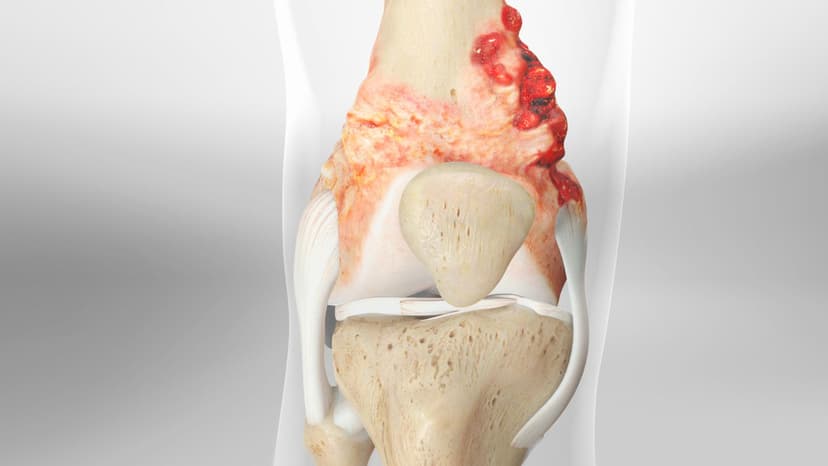
Best Clinics for Osteosarcoma Treatment Abroad
Patients who choose international treatment benefit not only from high success rates and cutting-edge therapies but from personalized care, advanced diagnostics, and access to clinical trials. Below a...

Switzerland’s Best Clinics for Torn Ligament Treatment
Switzerland is renowned for its exceptional healthcare system and access to advanced medical technologies. The country’s orthopedic and sports medicine clinics are globally recognized for their expert...
Our doctor is highly skilled and an expert in their field.









